When to suspect a meningeal carcinomatosis?
A 62-year-old woman had a diagnosis of endometrial cancer. A week before she started with altered mental status, somnolence, together with nausea, vomiting and constipation. She had a fever one day.
The physical examination showed a woman disorientated.There was a herpetic lesion on the lower lip. Some rales were present in the right basal lung. A systolic murmur was present. The abdominal examination showed a bladder retention. She could move the arms and the legs. She looks dehydrated. She was afebrile.
Neurological examination: No neck stiffness was present. The patient could move her four legs, but without a voluntary action. No Babinski was present.
Analytical data: Blood test, kidney function, bilirrubin level, thyroid hormon function, glucose level and blood cultures were normal. The calcium level was increased(corrected value: 12,3 mg)
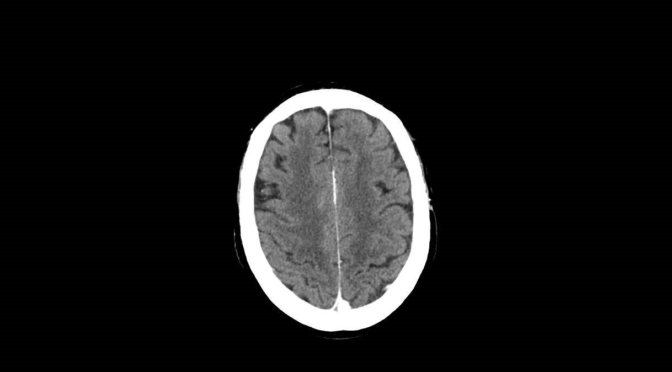
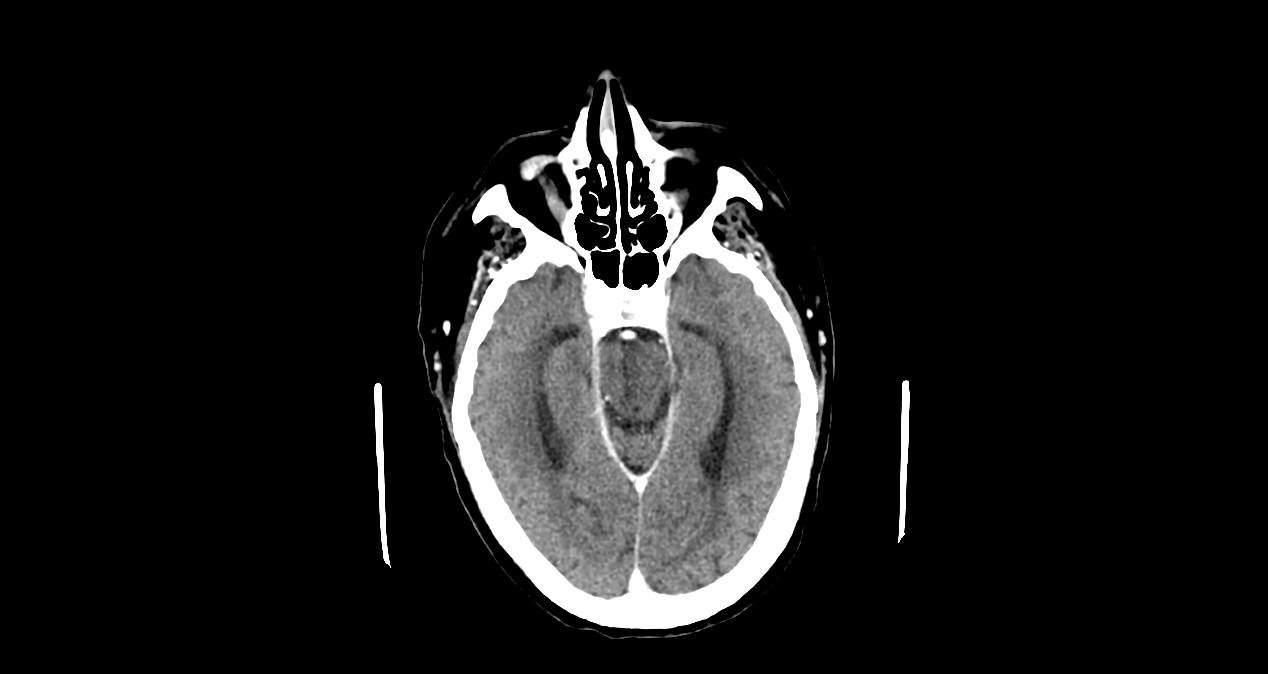
Image: CT scan without contrast was normal.
Lumbar puncture: Not made, due to clinical deterioration
Differential diagnosis: some clinical entities were considered such as hypercalcemia, sepsis, herpetic encephalitis, metastases, meningeal carcinomatosis, infectious meningitis
Final Diagnosis: meningeal carcinomatosis
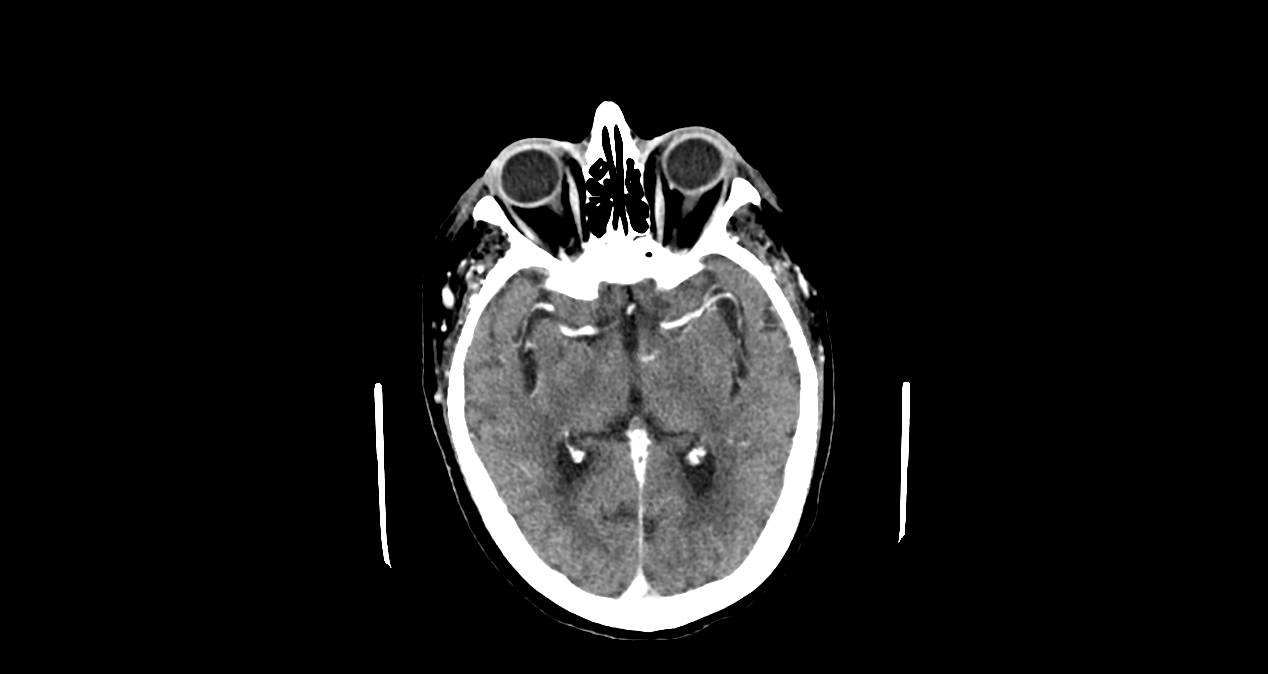
Comment: Meningeal carcinomatous is an insidious clinical situation. The diagnosis is usually made after detected the presence of neoplastic cells in the cerebrospinal fluid , but the level of false negative is high. The definitive diagnosis is established after specified signs detected in a Magnetic Nuclear Resonance or a CT scan with contrast.